 Pirates Creed is a dynamic duo composed of two best friends, known as the Navigator and the Quartermaster. They’re the masterminds behind the band’s unique sound, blending “grog rock” and “Sea Grass” music with a pirate twist. These two musicians have a long history of performing together, having met while playing in another pirate band at the Ohio Renaissance Festival. They decided to join forces and create Pirates Creed.
Pirates Creed is a dynamic duo composed of two best friends, known as the Navigator and the Quartermaster. They’re the masterminds behind the band’s unique sound, blending “grog rock” and “Sea Grass” music with a pirate twist. These two musicians have a long history of performing together, having met while playing in another pirate band at the Ohio Renaissance Festival. They decided to join forces and create Pirates Creed.
Author: savage
Thomas Tew
 Thomas Tew was one of the most well-known Red Sea pirates active in the 1690s. It is thought he was born in 1649, but it is unsure exactly where. Suggestions include Rhode Island in the American colonies and Northamptonshire in England, although evidence seems to be lacking for the latter. Whether from Rhode Island or not, it is believed Tew had family in Rhode island. He was thought to have been married with two daughters, one of whom was named Amity, living in Newport, Rhode Island. He is best known, along with other infamous pirates such as Henry Avery and William Kidd, for sailing the Pirate Round, a sailing route followed by certain pirates during the late 17th century leading from the western Atlantic, running parallel to the Cape Route around the southern tip of Africa until Madagascar. From there one could reach targets in the Red Sea and India.…
Thomas Tew was one of the most well-known Red Sea pirates active in the 1690s. It is thought he was born in 1649, but it is unsure exactly where. Suggestions include Rhode Island in the American colonies and Northamptonshire in England, although evidence seems to be lacking for the latter. Whether from Rhode Island or not, it is believed Tew had family in Rhode island. He was thought to have been married with two daughters, one of whom was named Amity, living in Newport, Rhode Island. He is best known, along with other infamous pirates such as Henry Avery and William Kidd, for sailing the Pirate Round, a sailing route followed by certain pirates during the late 17th century leading from the western Atlantic, running parallel to the Cape Route around the southern tip of Africa until Madagascar. From there one could reach targets in the Red Sea and India.…
Pirates and privateers
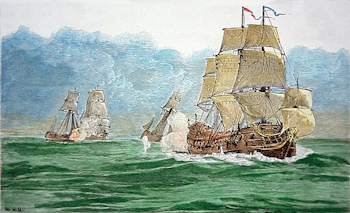 The terms pirate and privateer are unclear to many people, but there was a clear distinction which was made between the two in the past, even if a shadowy grey area did exist for many people. In fact, during the Age of Sail, one man’s privateer was often another man’s pirate. First we must look at what a pirate is. The word itself is derived with the Greek peiratēs, meaning brigand, and like a brigand or bandit there were no restrictions on whom they attacked. They were outlaws plain and simple, possessing no legal commission, or one which covered the specific act of aggression they carried out. They often had their own flags, usually only flying the flag of a nation under false colours to trick their prey, although those pirates who considered themselves patriots might have flown the flag of their own nation too. They usually obtained their vessel by means of mutiny or capture.…
The terms pirate and privateer are unclear to many people, but there was a clear distinction which was made between the two in the past, even if a shadowy grey area did exist for many people. In fact, during the Age of Sail, one man’s privateer was often another man’s pirate. First we must look at what a pirate is. The word itself is derived with the Greek peiratēs, meaning brigand, and like a brigand or bandit there were no restrictions on whom they attacked. They were outlaws plain and simple, possessing no legal commission, or one which covered the specific act of aggression they carried out. They often had their own flags, usually only flying the flag of a nation under false colours to trick their prey, although those pirates who considered themselves patriots might have flown the flag of their own nation too. They usually obtained their vessel by means of mutiny or capture.…
Jack Tar
Jack Tar: Life in Nelson’s Navy by Lesley Adkins & Roy Adkins
 The Royal Navy to which Admiral Lord Nelson sacrificed his life depended on thousands of sailors and marines to man the great wind-powered wooden warships. Drawn from all over Britain and beyond, often unwillingly, these ordinary men made the navy invincible through skill, courage and sheer determination. They cast a long shadow, with millions of their descendants alive today, and many of their everyday expressions, such as ‘skyscraper’ and ‘loose cannon’, continuing to enrich our language. Yet their contribution is frequently overlooked, while the officers became celebrities.
The Royal Navy to which Admiral Lord Nelson sacrificed his life depended on thousands of sailors and marines to man the great wind-powered wooden warships. Drawn from all over Britain and beyond, often unwillingly, these ordinary men made the navy invincible through skill, courage and sheer determination. They cast a long shadow, with millions of their descendants alive today, and many of their everyday expressions, such as ‘skyscraper’ and ‘loose cannon’, continuing to enrich our language. Yet their contribution is frequently overlooked, while the officers became celebrities.
JACK TAR gives these forgotten men a voice in an exciting, enthralling, often unexpected and always entertaining picture of what their life was really like during this age of sail. Through personal letters, diaries and other manuscripts, the emotions and experiences of these people are explored, from the dread of press-gangs, shipwreck and disease, to the exhilaration of battle, grog, prize money and prostitutes. …



