 By the time the Great Fire occurred, London was by far the largest city in England. Its inhabitants numbering between 300,000 and 400,000, it had become a crowded, unregulated sprawl of houses. This wasn’t the first large scale fire, the city having experienced several major fires in the past, the most recent having been in 1633. Additionally, London had been hit by an epidemic of bubonic plague called the Great Plague of London only the year before, during which between 60,000 and 100,000 are thought to have died. As well as disease, fires were always a danger in a city made mostly of timber and tar paper. There were so many possible causes: fireplaces, candles, ovens, lamps, as well a large stores of combustibles such as pitch and hemp. To combat the perpetual danger, there were watchmen, also known as bellmen, who patrolled the city at night, who sounded the alarm should a fire break out.…
By the time the Great Fire occurred, London was by far the largest city in England. Its inhabitants numbering between 300,000 and 400,000, it had become a crowded, unregulated sprawl of houses. This wasn’t the first large scale fire, the city having experienced several major fires in the past, the most recent having been in 1633. Additionally, London had been hit by an epidemic of bubonic plague called the Great Plague of London only the year before, during which between 60,000 and 100,000 are thought to have died. As well as disease, fires were always a danger in a city made mostly of timber and tar paper. There were so many possible causes: fireplaces, candles, ovens, lamps, as well a large stores of combustibles such as pitch and hemp. To combat the perpetual danger, there were watchmen, also known as bellmen, who patrolled the city at night, who sounded the alarm should a fire break out.…
Category: Historical
Leisler’s Rebellion
 Leisler’s Rebellion took place in New York in 1689. New York had only become an English colony in 1664 during the reign of James II. It previously had the name New Amsterdam and was part of the Dutch colony New Netherlands. After the Director-General Peter Stuyvesant surrendered to English troops, the Dutch residents were permitted to remain in the colony and were granted religious freedom. The Dutch briefly regained the colony in 1673, but it became English again under the Treaty of Westminster, which ended the third Anglo-Dutch war. The governor of the colony of New York wasn’t keen to allow an elected representative assembly, instead letting it effectively be ruled by an oligarchy of wealthy merchants. In 1688 New York became a part of the Dominion of New England, governed by Sir Edmond Andros, who governed in an autocratically with no elected legislature.
Leisler’s Rebellion took place in New York in 1689. New York had only become an English colony in 1664 during the reign of James II. It previously had the name New Amsterdam and was part of the Dutch colony New Netherlands. After the Director-General Peter Stuyvesant surrendered to English troops, the Dutch residents were permitted to remain in the colony and were granted religious freedom. The Dutch briefly regained the colony in 1673, but it became English again under the Treaty of Westminster, which ended the third Anglo-Dutch war. The governor of the colony of New York wasn’t keen to allow an elected representative assembly, instead letting it effectively be ruled by an oligarchy of wealthy merchants. In 1688 New York became a part of the Dominion of New England, governed by Sir Edmond Andros, who governed in an autocratically with no elected legislature.
The War of the Quadruple Alliance (1718-1720)
 Although a Bourbon king, Philip V, took the throne of Spain after the War of Spanish Succession came to an end, Spain had been forced to give up territory in Italy and the Spanish Netherlands under the 1713 Peace of Utrecht. In 1718, the Spanish wanted to recover some of that lost land. As a result, the conflict known as the War of the Quadruple Alliance broke out between Spain and a coalition consisting of Great Britain, France, and Savoy, later joined by Austria after they had signed peace with the Ottomans. The Dutch Republic also joined the coalition in 1719. The war took place mainly in Sicily and northern Spain with some minor engagements in North America. Additionally, the Spanish supported Jacobite rising of 1719 in Scotland, which is considered to be a part of this conflict.
Although a Bourbon king, Philip V, took the throne of Spain after the War of Spanish Succession came to an end, Spain had been forced to give up territory in Italy and the Spanish Netherlands under the 1713 Peace of Utrecht. In 1718, the Spanish wanted to recover some of that lost land. As a result, the conflict known as the War of the Quadruple Alliance broke out between Spain and a coalition consisting of Great Britain, France, and Savoy, later joined by Austria after they had signed peace with the Ottomans. The Dutch Republic also joined the coalition in 1719. The war took place mainly in Sicily and northern Spain with some minor engagements in North America. Additionally, the Spanish supported Jacobite rising of 1719 in Scotland, which is considered to be a part of this conflict.
Lost Spanish treasure fleet 1715
 On 31st July 1715 a Spanish treasure fleet sank during a hurricane off the east coast of Florida. It was a catastrophe for the Spanish Crown, which was heavily relying on its cargo. The galleons were fully loaded with precious cargoes of gold, silver, jewellery, tobacco, spices, indigo, cochineal etc. The Spanish government was relying its the safe arrival, as the War of Spanish Succession, which had hindered the sailing of the treasure fleets, had just come to an end. For obvious reasons, this disaster awoke the interest of pirates, privateers, and honest seamen alike.
On 31st July 1715 a Spanish treasure fleet sank during a hurricane off the east coast of Florida. It was a catastrophe for the Spanish Crown, which was heavily relying on its cargo. The galleons were fully loaded with precious cargoes of gold, silver, jewellery, tobacco, spices, indigo, cochineal etc. The Spanish government was relying its the safe arrival, as the War of Spanish Succession, which had hindered the sailing of the treasure fleets, had just come to an end. For obvious reasons, this disaster awoke the interest of pirates, privateers, and honest seamen alike.
The Spanish treasure fleets
 Treasure fleets consisting of a dozen or more ships used to sail from Cádiz or Seville in Spain, bringing European goods not readily available in the New World to the colonies with the aim of returning with gold, silver and other goods from Peru and Colombia, as well as spices and other items from south east Asia, brought across the Pacific by the Manila Galleon, which was then transported by mule train across the isthmus of Panama.…
Treasure fleets consisting of a dozen or more ships used to sail from Cádiz or Seville in Spain, bringing European goods not readily available in the New World to the colonies with the aim of returning with gold, silver and other goods from Peru and Colombia, as well as spices and other items from south east Asia, brought across the Pacific by the Manila Galleon, which was then transported by mule train across the isthmus of Panama.…
Palmares
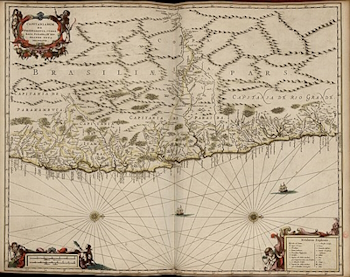 In the early 17th century an autonomous, self-sufficient community of escaped slaves (maroons) known as Palmares established itself in the Captaincy of Pernambuco in north-eastern Brazil. It grew considerably throughout the 17th century, eventually becoming the largest settlement ever founded by runaway slaves in Brazil. Most of the information about this community comes from Portuguese and Dutch colonists and many of the names of those involved are unknown. At its apex, the population of Palmares reached somewhere between 10,000 and 20,000. The Palmaristas constantly resisted Portuguese and Dutch attacks while at the same time carrying out their own raids on the colonists. In the 1500s nearly half of all those enslaved from Africa were transported to Brazil, which was governed by the Portuguese at the time. Their settlements, called mocambos or quilombos, were constructed in the land’s interior, although the later is a modern term. At its height in the 1660s, Quilombo of Palmares was a confederation with a central capital and associated fortified towns and villages.…
In the early 17th century an autonomous, self-sufficient community of escaped slaves (maroons) known as Palmares established itself in the Captaincy of Pernambuco in north-eastern Brazil. It grew considerably throughout the 17th century, eventually becoming the largest settlement ever founded by runaway slaves in Brazil. Most of the information about this community comes from Portuguese and Dutch colonists and many of the names of those involved are unknown. At its apex, the population of Palmares reached somewhere between 10,000 and 20,000. The Palmaristas constantly resisted Portuguese and Dutch attacks while at the same time carrying out their own raids on the colonists. In the 1500s nearly half of all those enslaved from Africa were transported to Brazil, which was governed by the Portuguese at the time. Their settlements, called mocambos or quilombos, were constructed in the land’s interior, although the later is a modern term. At its height in the 1660s, Quilombo of Palmares was a confederation with a central capital and associated fortified towns and villages.…
